How to Avoid Plagiarism: The Writer’s Guide to Original Work

To avoid plagiarism, practice thorough note-taking, summarize ideas in your own words, and always credit your sources, even when paraphrasing. Understand that plagiarism includes not just copying text, but also mosaic plagiarism and self-plagiarism. True paraphrasing involves deeply understanding the source and expressing the idea in a new, original way. Using plagiarism checkers and managing your time effectively also help ensure your work stays authentic and properly cited.
Understanding Plagiarism Beyond the Obvious
Plagiarism isn’t always as simple as copying and pasting. Sure, outright duplication is a big no-no, but there are other, sneakier forms of plagiarism that can catch even experienced writers off guard. I’ve talked to professors and writers who’ve been surprised by these gray areas. One common trap is mosaic plagiarism. Think of it like building a Frankenstein essay—you’re patching together phrases from different sources without giving credit where it’s due. It might look like a complete piece, but it’s lacking that crucial original spark.
Another tricky one is self-plagiarism. Reusing your own past work might seem harmless—after all, it’s your brilliant idea, right? But submitting the same paper for different assignments usually isn’t allowed. It’s generally seen as academic dishonesty.
Paraphrasing can also lead to plagiarism if you’re not careful. Simply swapping a few synonyms doesn’t cut it. Real paraphrasing means understanding the original idea deeply and explaining it in your own words. If you’re curious about using AI writing tools responsibly, you might find this guide helpful: Check out our guide on using AI without plagiarizing. All this worry about plagiarism is a big reason why plagiarism checker tools are becoming so popular. The market for these tools is booming. It was valued at about USD 0.22 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 0.56 billion by 2033. You can find more details here: Discover more insights. This shows a real need for effective anti-plagiarism solutions.
Finally, cultural differences can affect how plagiarism is viewed. What’s okay in one culture might be considered plagiarism in another. Understanding these differences is key when you’re navigating academic or professional writing. Having good intentions is important, but it doesn’t automatically mean your work is plagiarism-free. Recognizing these less obvious types of plagiarism is the first step to creating truly original work.
Smart Research Habits That Prevent Problems Later
The secret to avoiding plagiarism isn’t about memorizing every single citation style. It’s about building smart research habits from the get-go. I’ve seen way too many writers treat research like a frantic race to find quotable gems, instead of a thoughtful exploration of ideas. Trust me, this sets you up for plagiarism headaches down the road. Effective research is more like having a conversation with the material. It’s about truly grasping the core concepts and then synthesizing them into something fresh and new.
One crucial habit is taking purposeful notes. Don’t just copy and paste huge chunks of text. Summarize the key points in your own words. This forces you to actively engage with the information, making it stick. Also, be meticulous about keeping track of your sources. I personally use a tagging system for each note, including the author, title, and publication date. It’s a lifesaver when it comes to citing correctly. Understanding the difference between intellectual property protections like trademark vs copyright is also essential.
Another vital skill is synthesizing information. This involves weaving insights from multiple sources together to create a unique perspective. Think of it like baking a cake. You use individual ingredients (your sources) to create something completely different and delicious (your original work). This naturally leads to original thinking and reduces the risk of over-relying on a single source. For example, when writing about climate change, you could combine data from scientific reports with the viewpoints of economists and sociologists to build a more nuanced and well-rounded argument.
To help visualize different note-taking methods and their role in plagiarism prevention, take a look at this comparison table:
Note-Taking Methods Comparison: A comparison of different note-taking approaches and their effectiveness in preventing plagiarism.
| Method | Plagiarism Prevention Level | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summarizing | High | Understanding core concepts | Forces engagement with the material, promotes paraphrasing | Can be time-consuming |
| Paraphrasing | High | Restating ideas in your own words | Encourages original thought, helps avoid direct copying | Requires careful attention to meaning |
| Quoting (Sparingly) | Medium | Highlighting key phrases | Provides impact, supports arguments | Overuse can lead to plagiarism |
| Copy-Pasting (with clear source attribution for later review and rewriting) | Low (unless rewritten later) | Quickly gathering information | Saves time initially | High risk of plagiarism if not rewritten |
This table highlights the importance of active engagement with your source material through summarizing and paraphrasing for the best plagiarism prevention. While quoting has its place, relying too heavily on it can be risky. Copy-pasting, even with attribution, should be treated with extreme caution and always rewritten.
Finally, don’t be afraid to let your own voice shine through. Your perspective is what makes your writing truly yours, even when using multiple sources. Your analysis, the connections you draw between ideas, your conclusions—these are all original contributions. This ownership is the best defense against plagiarism. It’s not just about avoiding copied phrases; it’s about putting your unique intellectual stamp on your work. This builds confidence and naturally steers you away from unintentional plagiarism.
Paraphrasing That Actually Transforms Ideas
Let’s be real, most people think swapping out “big” for “large” is paraphrasing. It’s not. It’s a word game, and it won’t fool anyone, especially not plagiarism checkers. Real paraphrasing is more like translating – taking an idea from the original source and expressing it in your own unique voice.
Think about it like this: you’re reading a biology textbook, and it says, “Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell.” Changing it to “Mitochondria provide energy to the cell” isn’t true paraphrasing. The bones are the same. A better approach? Try something like, “Imagine tiny power plants inside each cell – that’s what mitochondria are, constantly churning out the energy that keeps us going.” See the difference?
This kind of in-depth understanding is crucial. You have to grasp the core concept well enough to explain it in a completely different way. That means changing not just the words, but also the sentence structure and how you present the information. Ask yourself, “What’s the author’s main point?” and then explain it as you would to a friend over coffee.
Now, sometimes an author nails the phrasing so perfectly that any change feels like a downgrade. In those cases, a direct quote is your best friend. Just remember the quotation marks and the proper citation. Over-citing is way better than under-citing, trust me. Need more paraphrasing tips? Check out this helpful resource: Learn more in our article about how to paraphrase to avoid AI detection.
The goal is to transform the idea itself, not just the words on the page. This makes your writing stronger and keeps you clear of plagiarism. By truly making the idea your own, you’re showing real understanding and adding your unique perspective to the conversation.
Citation Without the Headache
I know, I know – citations. They can feel like a real drag. But trust me, they’re more than just a formality. They’re your secret weapon for building credibility and showing your audience you’ve actually done your research. Think of them as little signposts pointing back to where you got your info. They don’t interrupt your flow, they actually make it stronger by adding context and depth. And honestly, knowing when to cite is a huge part of avoiding plagiarism. It’s probably more often than you think!
Whenever you’re using someone else’s idea – whether it’s a direct quote, a paraphrased point, or even just a statistic – you have to give them credit. Obviously, common knowledge (like, the sky is blue) doesn’t need a citation. But if you’re using specific facts, data, or interpretations, citations are a must. This protects you from plagiarism accusations, sure, but it also lets your readers dive deeper into the stuff that they find interesting.
For example, imagine you’re writing about the effects of social media on teens. If you mention a study, including a citation lets your readers find that study and explore the results themselves. That kind of transparency makes your writing stronger because it’s built on a solid foundation.
Proper citation isn’t just about staying out of trouble; it’s about joining the conversation. When you cite a source, you’re showing how your ideas connect to existing research. It’s like saying, “I’m building on this great work, and here’s where you can find it.” That builds trust with your readers and helps them understand how you arrived at your conclusions. It also shows you know what you’re talking about. Speaking of which, if you’re worried about how AI detection fits into all this, this might be helpful: You might be interested in: How to avoid AI detection in writing.
Even seasoned writers sometimes run into tricky citation situations. Like, what about that insightful tweet you want to use, or a blog post with no clear author? Don’t worry, there are specific rules for those situations, which we’ll cover later. For now, remember that all sources – even the unusual ones – deserve credit. It’s a matter of intellectual honesty. The global anti-plagiarism software market is a USD 1646.46 million industry as of 2024, projected to reach USD 10,517.67 million by 2033 (a 20.1% CAGR), which tells you something about how important this is. Read the full research. At the end of the day, good citations build your reputation as a careful and trustworthy writer. It’s a small thing with a big impact.
Making Plagiarism Checkers Work for You
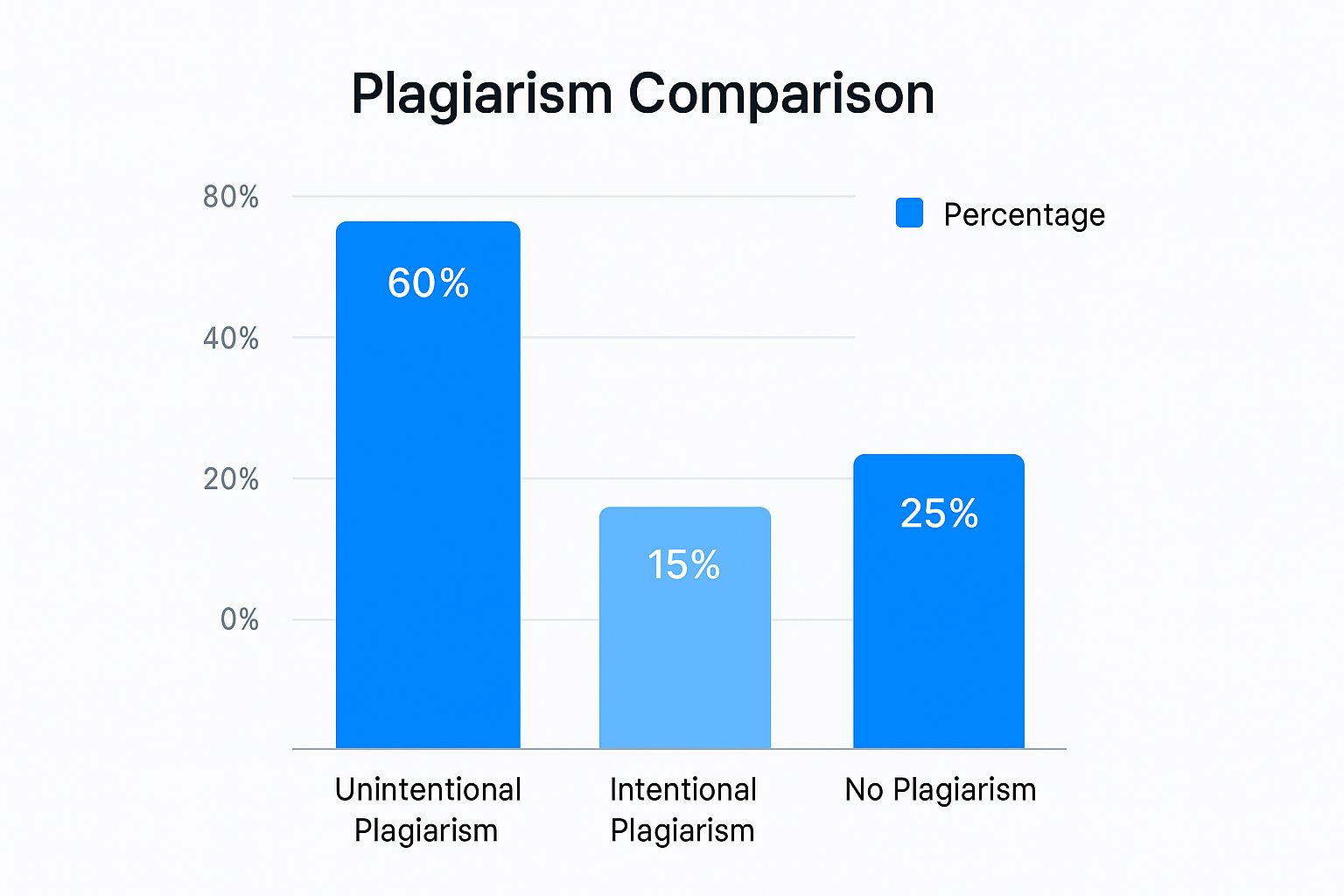
The infographic above shows how often different types of plagiarism pop up. Unintentional plagiarism takes the lead at 60%. This just goes to show how easy it is to accidentally plagiarize, even when you’re trying your best not to. Intentional plagiarism comes in at 15%, while 25% of work is plagiarism-free. Knowing how plagiarism checkers work is essential for navigating these tricky waters.
Plagiarism checkers aren’t perfect. I’ve seen them flag perfectly original work while completely missing blatant copying. They can also cause a lot of unnecessary stress over tiny similarities. Knowing their limits is the key to using them effectively. There’s a huge difference between free tools like the basic Grammarly plagiarism checker and the more powerful platforms used by universities and employers.
For example, Turnitin, a popular choice in academia, gives you detailed similarity reports and checks against massive databases.
This screenshot shows a typical Turnitin interface. See how clearly it presents the similarity scores? It also provides tools for digging deeper into the flagged sections. Being able to interpret those scores (a 15% match isn’t always a problem!) is so important for avoiding unnecessary stress.
Understanding Plagiarism Checker Reports
When you’re dealing with citations, these essential tips for successful grant writing can be surprisingly helpful. Learning to investigate those flagged sections and tell the difference between a real problem and a false alarm will save you time and headaches.
You also need to be aware of the privacy implications. Where is your writing going? Who can see it? These are good questions to ask. Developing your own internal “plagiarism radar”—that feeling that something’s just not right—is invaluable. You might find this interesting: Read also: How to bypass AI detection.
The market for plagiarism checker software is huge, estimated at USD 91,254.2 million in 2024. That shows how much we need these tools! Discover more insights.
Here’s a quick comparison of some popular plagiarism checkers to help you choose the right one for your needs:
Popular Plagiarism Detection Tools Comparison: A detailed comparison of features, pricing, and effectiveness of leading plagiarism checkers.
| Tool Name | Free Version Available | Key Features | Best For | Accuracy Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grammarly | Yes | Basic plagiarism detection, grammar and style checking | Casual writing, quick checks | Moderate |
| Turnitin | No | In-depth similarity reports, extensive databases, institutional subscriptions | Academic writing, professional use | High |
| ProWritingAid | Limited | Grammar and style checking, plagiarism detection, writing reports | Bloggers, fiction writers | Moderate |
| Quetext | Limited | Deep search technology, contextual analysis, plagiarism score | Students, educators, professionals | High |
This table highlights some key differences between these tools. Notice how some are free, while others offer limited free versions. The features and accuracy also vary, so choosing the right one depends on what you need.
Creating Your Personal Integrity System
Learning how to avoid plagiarism isn’t just about acing that next paper. It’s about building a writing practice that’s all about authenticity. Think of it as developing your own personal integrity system. One that’s so ingrained, it works even when you’re stressed, tired, or facing a fast-approaching deadline.
Time Management and Source Integration
Good writing takes time. Experienced writers know this and they don’t cram research and writing into the last minute, throwing citations together as an afterthought. They schedule time for proper source integration.
This means taking thorough notes, summarizing key points in their own words, and carefully tracking the origin of each piece of information. Using online tools like Copyscape to double-check work is also a good idea. This kind of deep engagement with the material naturally reduces the temptation to plagiarize.
Finding Your Unique Voice
Even when you’re juggling multiple sources, keeping your own voice is crucial. This goes beyond simply avoiding copied phrases. It’s about bringing your own perspective and analysis into the mix. Your interpretation, the connections you make, how you frame the arguments – that’s what makes your work truly yours.
For example, I once wrote a paper on social media’s impact on political discourse. I used a lot of sources, sure, but I focused on how different platforms create unique communication styles, and then drew my own conclusions about what that means for democracy. This sense of ownership is key, not only for originality but also for building confidence in your analytical skills.
Overcoming Writer’s Block
We’ve all been there. Blank page, looming deadline, and the siren call of copy-and-paste. In these moments, stepping away can be the best thing you can do. Go for a walk, listen to some music, or try freewriting to get your creative juices flowing.
Remember, even when your ideas feel stale, your perspective is still unique. By focusing on expressing your understanding, even simply, you can push past that writer’s block and maintain your integrity. Building in some accountability can also help. Try sharing drafts with a friend or keeping a writing journal to track your progress and challenges. It’s a great way to stay on track and resist the plagiarism temptation.
Ready to unlock your writing potential and create original, engaging content effortlessly? Try Word Spinner free for five days and experience the power of AI-assisted writing without the worry of plagiarism. Start your free trial today!